Ulcerative Colitis
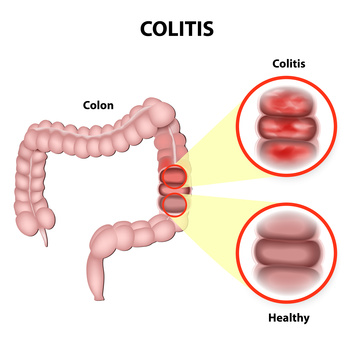
Dr. Fishbein uses the most current and innovative medical approaches to the management of ulcerative colitis. He uses so called “Treat To Target” approach with individually tailored therapy. Ulcerative colitis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the rectum and large intestine. Inflammation may begin in the rectum and lower intestine often progresses to involve the entire colon.
UC can happen at any age, but it usually starts between the ages of 15 and 30. It tends to run in families. The most common symptoms are pain in the abdomen and blood or pus in diarrhea.
Symptoms
A patient may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
• Abdominal pain
• Bloody diarrhea
• Rectal bleeding
• Fever
• Weight loss
• Sometimes there is a joint, skin or liver disease associated.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis requires the following:
1. Your doctor will ask for a complete medical history and will perform a thorough physical examination.
2. Your doctor may order a series of tests that will help to confirm a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. These may include:
Blood tests
Colonoscopy. A flexible tube with a camera and light attached at the tip is gently advanced through the anus, rectum and colon to view the lining of the colorectum and take appropriate biopsies. Your doctor can examine the inside of the colon carefully, looking for signs of disease.
Upper endoscopy or upper GI x- rays are sometimes employed to help rule out Crohn’s disease.
Treatment
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis are managed through medications as long as there is a favorable response. Patients with ulcerative colitis have a higher risk of cancer and must have regular check-ups for the rest of their lives.
Surgery
Surgery is reserved for patients with disabling symptoms, which are not controlled by medications or those with an increased cancer risk. Cancer risk is determined by finding dysplasia (pre-cancer) in biopsies taken during check-ups by colonoscopy.
When surgery for ulcerative colitis is necessary the entire colon and rectum are removed so there can no incidence of colitis.
Learn more about colon and rectal surgery.
